On Tuesday, the nation’s toughest law on abortion drugs took effect in Arizona. The measure—which passed the state legislature in 2012 but was temporarily blocked by a federal lawsuit—requires doctors to prescribe the most common abortion pill, RU468 or mifepristone, exactly as called for on its 14-year-old FDA label. Studies by the World Health Organization and independent scientists have since found that the drug works equally well at a third the original dose. It can also be safely used nine weeks into pregnancy, rather than just seven, as the label states. Both the WHO and the American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists have updated their guidelines accordingly, with lower doses and fewer doctors’ visits than suggested by the FDA.
By compelling healthcare providers to stick to the outdated label, Arizona will make medication abortions—which can be performed earlier than other readily available options—more expensive and difficult to access. The Arizona law also requires that a doctor be present when the pills are taken. Women’s health advocates say this will make it impossible for some women in rural areas, where doctors and abortion clinics are scarce, to access abortions at all.
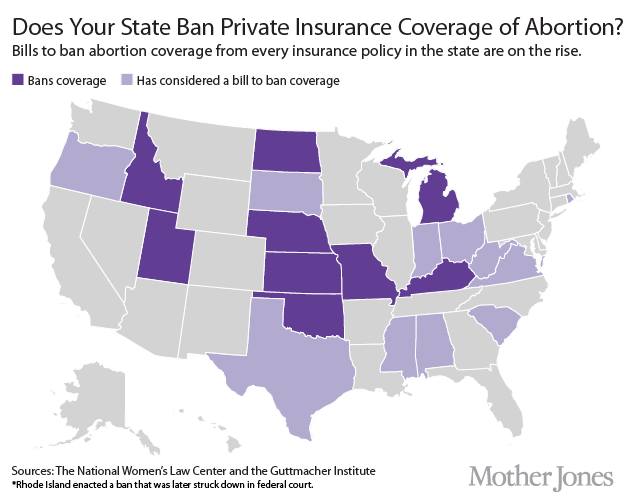
Arizona is hardly the only state to clamp down on abortion drugs. According to the Guttmacher Institute, in recent years at least 39 states have passed bills limiting access. Below is a state-by-state breakdown.
A state-by-state LOOK AT abortion drug restrictions
Hover over a state to see a breakdown of restrictions in place there. Source: Guttmacher Institute.