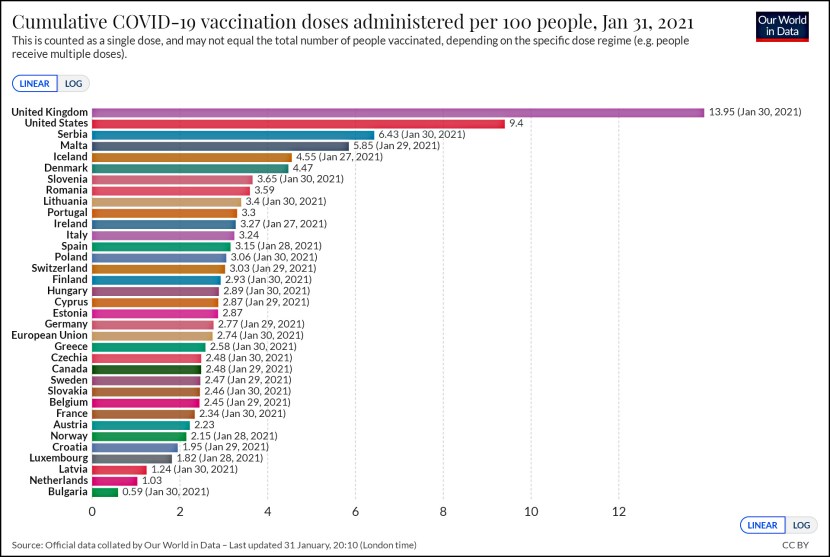
Danielle Kurtzleben points to an interesting chart today from the White House’s Economic Report of the President. It’s based on only two data points (1977 and 2008), but it’s still kind of intriguing.
Since 1977, two things have happened. First, more women have entered the paid workforce. Second, more men have started doing housework. It’s hardly surprising, then, that both men and women report more work-family conflicts than they used to. But among 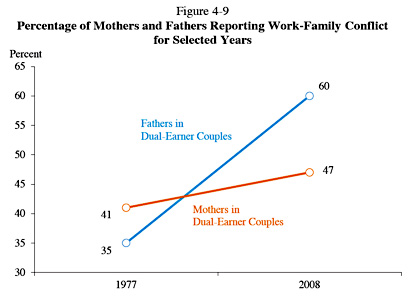 women, this number has gone up only 6 points. Among men, it’s gone up a whopping 25 points. Why the difference? Here are some possibilities:
women, this number has gone up only 6 points. Among men, it’s gone up a whopping 25 points. Why the difference? Here are some possibilities:
- In the period 1977-2008, female participation in the workforce went up only about 11 percentage points. So a rise of 6 points in work-family conflicts is within the range you’d expect.
- Men feel worse about adding housework to an existing job than women do about adding a paid job to existing housework. Some of this might be about the pay. Some of it might be about men feeling that housework is humiliating in some way. Some of it might be about workplaces being less sympathetic to men who want more flexibility for family reasons.
- “Conflict” can also be another word for guilt. There’s always a certain amount of badgering from the boss in any kind of job, and badgering from your wife might produce more feelings of resentment and guilt than badgering from your employer.
- Men are just bigger whiners than women.
I’d probably put my money on the first and third reasons—though the last one has a lot going for it too. And if I had to pick only one, I’d pick the first. Over the past few decades, there has just been way more growth in the number of men expected to do housework than in women entering the paid workforce. So it’s hardly surprising that there’s also more growth among men in work-family complaints.
But that’s just a guess. Feel free to school me in comments.