In honor of World Immunization Week, which begins this Thursday, UNICEF crunched the numbers on vaccines around the globe:
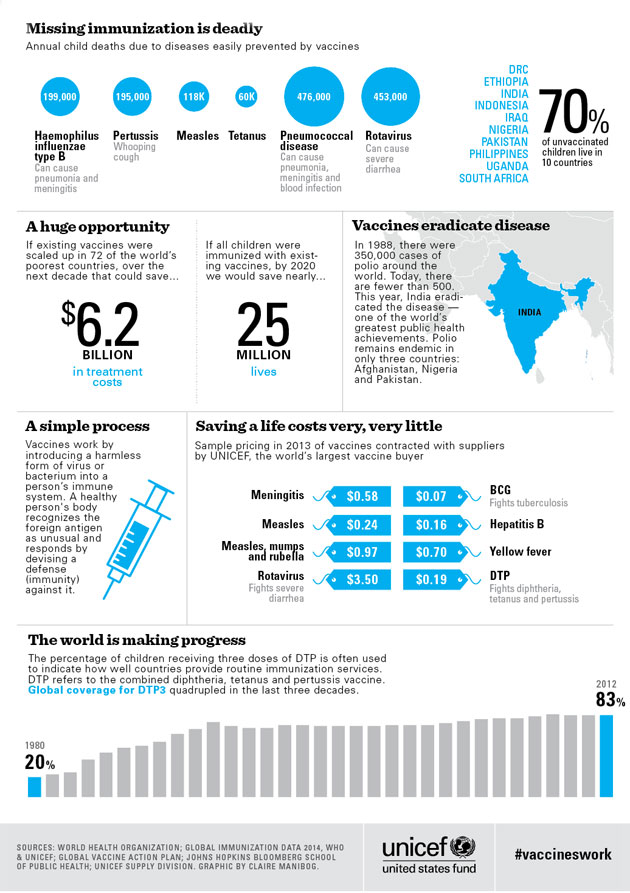
Click to enlarge. Image courtesy of UNICEF.
To me, that last graph is the most remarkable: We’ve more than quadrupled the global average routine immunization rate since 1980. But the hard work isn’t over. By 2020, UNICEF and the World Health Organization hope to increase that rate to 90 percent in every country in the world. In some places, that will be a heavy lift. In 2012, the last year for which UNICEF has data, the nations with the lowest rates of routine immunization in the world were Equatorial Guinea (33 percent), Nigeria (41 percent), and Chad (45 percent). By comparison, many countries in the European Union have rates of 99 percent, and the United States’ is 95 percent.
Jos Vandelaer, UNICEF’s chief of immunizations, notes that even when a country has eradicated a disease, it’s important to keep vaccinating children against it. Polio has been eradicated in every nation except Afghanistan, Pakistan, and Nigeria—and yet, in the past year, there have been cases of the disease in the Horn of Africa, Syria, and Iraq. By analyzing those recent cases, scientists determined that they were caused by the same strain of virus present in the three countries where the disease is still endemic. That means that the recent cases were imported—and that herd immunity is not yet strong enough in the Horn of Africa, Syria, or Iraq to prevent outbreaks.
That problem isn’t limited to the developing world; we’re seeing the same phenomenon with measles right here in the United States. “The virus finds the children who are not immune,” says Vandelaer. “And then you see outbreaks.”