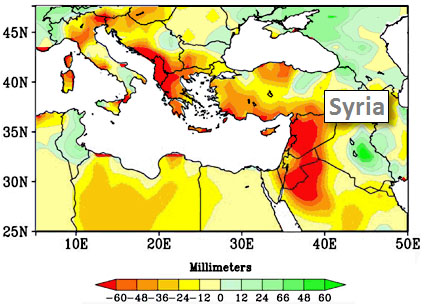
 Brad Plumer interviews Francesco Femia of the Center for Climate and Security, who points out that Syria has not only suffered a serious drought for the past five years, but that this has been no ordinary drought:
Brad Plumer interviews Francesco Femia of the Center for Climate and Security, who points out that Syria has not only suffered a serious drought for the past five years, but that this has been no ordinary drought:
We found it very interesting that right up to the day before the revolt began in Daraa, many international security analysts were essentially predicting that Syria was immune to the Arab Spring. They concluded it was generally a stable country. What they had missed was that a massive internal migration was happening, mainly on the periphery, from farmers and herders who had lost their livelihoods completely.
….In 2011 [the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration] released a report showing that a prolonged period of drying in the Mediterranean and the Middle East was linked to climate change. It was in line with previous projections. And on their map, Syria was colored bright red, meaning it had experienced the worst drying in the region. That really told us we needed to look at these dynamics.
The interview is full of the usual caveats, and you should read it. In particular, no one thinks drought directly caused the Syrian civil war, which might have been inevitable at some point thanks to the fault lines in Syrian society that mirror those in many other Middle Eastern countries. However, the stresses caused by extended drought might very well have affected the timing.
Climate scientists have been warning for over a decade that global warming is going to produce environmental stresses and severe weather patterns that will have devastating impacts on countries that are none too stable to begin with. As always, there will never be proof that any particular war is due solely or even primarily to climate change, just as no particular hurricane is ever solely the product of climate change. But the evidence is striking—and getting more striking all the time—that climate change very likely plays a role.