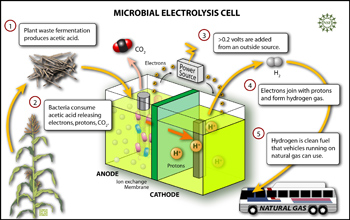
Researchers at Penn State University have coaxed common bacteria to produce hydrogen in a new, efficient way. Using starter material that could theoretically be sourced from a salad bar, the team has charmed bacteria from wastewater into generating abundant, clean hydrogen from cellulose or vinegar with a little zap of electricity. In a table-top reactor, no less.
Other systems produce hydrogen on a larger scale, reports the National Science Foundation, but few if any match the new system for energy efficiency. Even with the small jolt of electricity, the hydrogen provides more energy as fuel than the electricity needed to drive the reactor. The overall efficiency of the vinegar-fueled system is better than 80 percent, far better than the efficiency generating the leading alternative, ethanol. By perfecting the environment for the bacteria to do what they already do in nature, the new approach can be three to ten times more efficient than standard electrolysis.
Good news. And further proof that bacteria are our friends.
Julia Whitty is Mother Jones’ environmental correspondent. You can read from her new book, The Fragile Edge, and other writings, here.
















