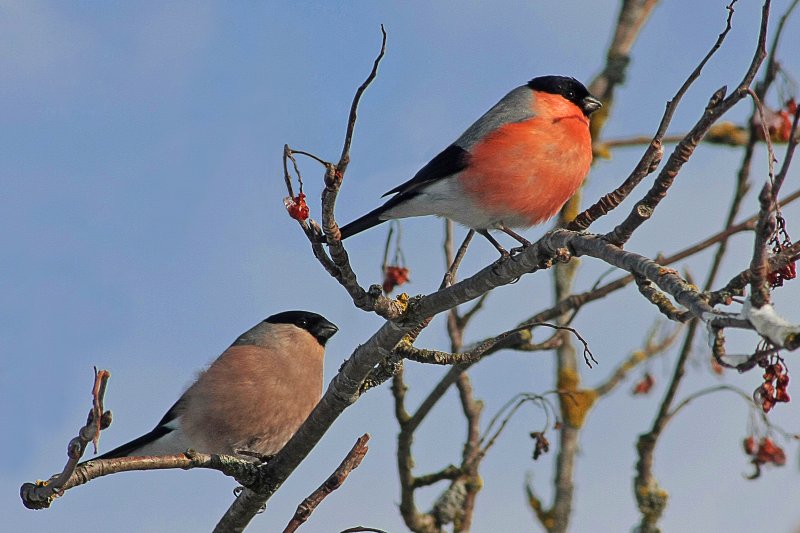
Eurasian bullfinch (Pyrrhula pyrrhula)Credit: Geli via <a href="http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pyrrhula_pyrrhula_-Germany_-perching_in_a_garden_tree_-pair-8a.jpg">Wikimedia Commons</a>.
Bird populations in Japan’s Fukushima Prefecture appear to be more whacked by the effects of low-level radiation than expected—based on responses by the same species around Chernobyl after that nuclear power plant disaster. This according to a new paper in the science journal Environmental Pollution.
Last July, four months after the earthquake and tsunami, a team of European, Japanese, and American researchers identified and counted birds at 300 locations in Fukushima prefecture between 15 and 30 miles (25 and 48 km) from the nuclear complex. Most of these areas were still open to human occupation and were experiencing external radiation levels from 0.5 to 35 microsieverts per hour.
The team compared the results to their similar investigation in the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone between 2006 and 2009, 20 to 23 years after that nuclear disaster.
Their findings:
- Overall, as expected, the bird community in Fukushima declined significantly in the more contaminated areas.
- For 14 species of birds that appeared in both Fukushima and Chernobyl, the decline in population size was more pronounced at Fukushima than Chernobyl.
- Among all birds, including the species not common to both areas, more birds declined in Chernobyl than Fukushima.
Why these discrepancies? Possibilities include:
- The Fukushima birds have never experienced radiation of this intensity before and may therefore be especially sensitive to radioactive contaminants.
- Overall more birds declined at Chernobyl because it’s been more than two decades since that disaster, during which many species have basically disappeared from the most contaminated regions.
Neither of those possibilities bode well for Fukushima’s birds in the long run.
The authors note that the March 11, 2011 nuclear accident at Fukushima occurred at the height of the main breeding season when birds were working at or close to their maximum sustainable level of energy output. Though presumably the Chernobyl birds, hit by radiation beginning on April 26, 1986, were experiencing similar stressors.
According to senior author Timothy Mousseau at the University of South Carolina’s College of Arts and Sciences:
Our results point to the need for more research to determine the underlying reasons for differences among species in sensitivity, both initially and following many generations of exposure… [and that] large-scale studies be initiated in Fukushima immediately to make the research potentially much more revealing.
The paper:
- Anders Pape Møller, Atsushi Hagiwara, Shin Matsui, Satoe Kasahara, Kencho Kawatsu, Isao Nishiumi, Hiroyuki Suzuki, Keisuke Ueda, Timothy A. Mousseau. Abundance of birds in Fukushima as judged from Chernobyl. Env Poll. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.01.008.