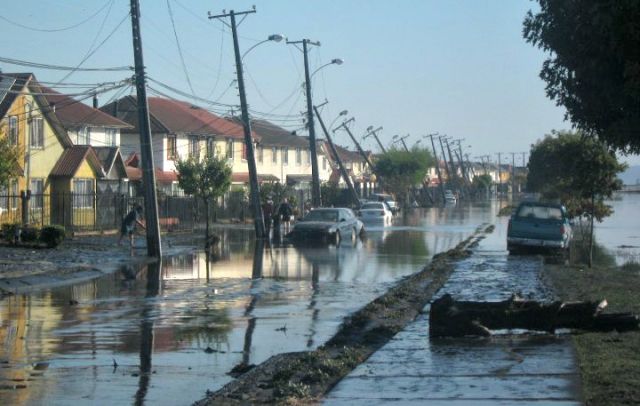
Chilean coastal town after the 2010 tsunami: Marcelo Caro via Wikimedia Commons
Chile’s 8.8 earthquake and tsunami of 2010 caused massive devastation, not least along its coastline, with some beaches subsiding and losing biodiversity, and some rocky reefs uplifting and losing biodiversity—as you might expect.
But thanks to the investigations of a science team already looking at the ecology of Chile’s sandy beaches before the quake, we now know this natural disaster also engineered some powerful and unexpected forms of coastal restoration.
This occurred where the temblor uplifted coastlines with coastal armouring—like seawalls and rocky revetments—which allowed those once-disappearing beaches to quickly grow where they had not grown in a long time, and allowed plants and other species to reinhabit places they hadn’t inhabited in a long time.
The study, just published in the open-access PLoS ONE, also previews the types of changes we might expect from climate warming and its accompanying sea level rise.
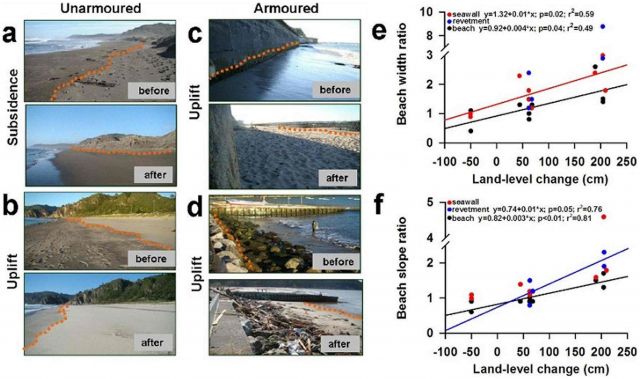 Photos of study sites taken before and after the 2010 Chile earthquake: Eduardo Jaramillo, et al. PLoS ONE. DOI:info:doi/10.1371/journal.pone.0035348.g001
Photos of study sites taken before and after the 2010 Chile earthquake: Eduardo Jaramillo, et al. PLoS ONE. DOI:info:doi/10.1371/journal.pone.0035348.g001
In the before-and-after disaster above the orange dotted lines indicate 24 hour spring high tide line. You can see that dry sandy areas above the high tide line dwindled where beaches that subsided (a) and increased where beaches uplifted (b, c and d). These changes were affected by whether or not coastal armoring was in place. Specifically:
- a–b show unarmored sites (a: where land subsided and the beach grew narrower after the quake; b: where coastal uplift made the beach wider afterwards)
- c–d show armored sites (c: where uplifted wider intertidal occurs in conjunction with a seawall; d: where uplifted wider intertidal occurs in conjunction with a revetment)
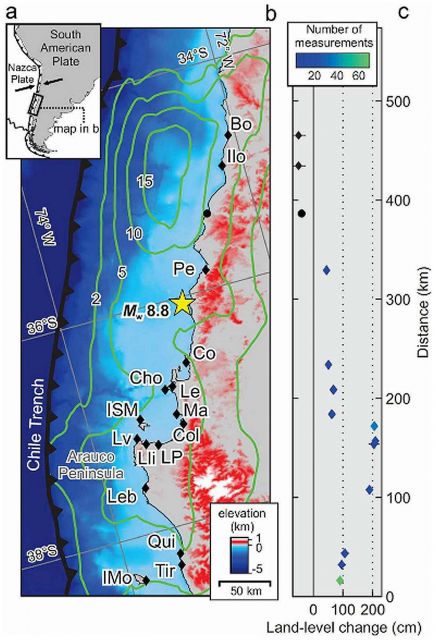
- e–f show relationships between the magnitude of land-level changes (e: shows beach widths; f: shows beach face slopes—red dots=sites with seawalls; blue dots=sites with rocky revetments; black dots=unarmored sites)
Land level changes from the 2010 Chile earthquake, epicenter yellow star: Eduardo Jaramillo, et al. PLoS ONE. DOI:info:doi/10.1371/journal.pone.0035348.g001
“So often you think of earthquakes as causing total devastation, and adding a tsunami on top of that is a major catastrophe for coastal ecosystems,” says co-author Jenny Dugan, at UCSB. “As expected, we saw high mortality of intertidal life on beaches and rocky shores, but the ecological recovery at some of our sandy beach sites was remarkable. Plants are coming back in places where there haven’t been plants, as far as we know, for a very long time. The earthquake created sandy beach habitat where it had been lost. This is not the initial ecological response you might expect from a major earthquake and tsunami.”
From the paper:
Ecological effects of extreme events, such those we observed for the [Chile] event, are expected to vary in duration. Shorter-term effects on beaches included direct mortality associated with the tsunami and the indirect bottom up effects of increased inputs of algal wrack from uplifted rocky shores on upper shore invertebrate consumers such as talitrid amphipods (Orchestoidea tuberculata). However, in areas with significant uplift (ca. 2 m), locations of armoring structures were shifted higher on the beach profile, reducing interaction with waves and tides and restoring intertidal zones for biota and ecological function. For this reason we expect positive changes observed in these beach ecosystems to persist, altering intertidal community composition and dynamics over the long term, even in front of existing coastal armoring. In contrast, for the subsided armored areas, community composition and population abundances are expected to remain depressed over time.
The paper:
- Jaramillo E, Dugan JE, Hubbard DM, Melnick D, Manzano M, et al. (2012) Ecological Implications of Extreme Events: Footprints of the 2010 Earthquake along the Chilean Coast. PLoS ONE 7(5): e35348. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0035348