Lightning over Brooklyn on October 11, 2010.<a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/60167034@N00/5073214755/">Arvind Grover</a>/Flickr
We know that droughts in parts of the country have likely been exacerbated by climate change and are expected to get worse in the future. But climate shifts are also causing bigger, badder rainstorms in other parts of the country, according to a new report Environment America released released on Tuesday.
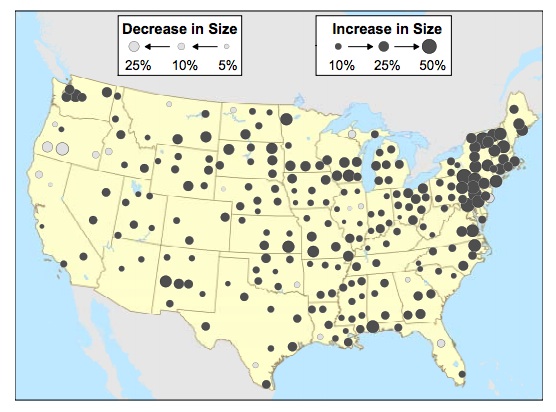
Extreme precipitation events are getting bigger, says the report, which is aptly titled, “When It Rains, It Pours”:
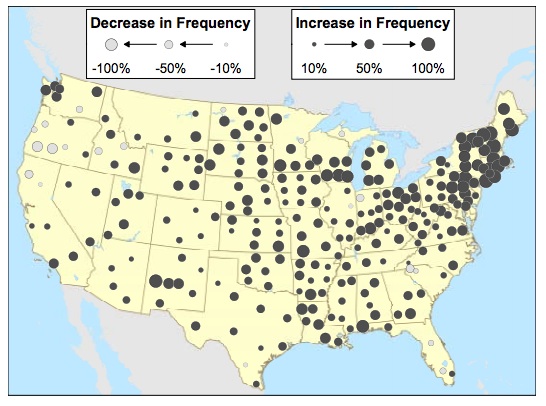
And big downpours are also happening more often:
To put together the report, Environment America looked at 80 million daily precipitation records in the US dating back to 1948, and found a 30 percent increase in the frequency of extreme rain- and snowstorms. That means that fierce downpours that used to happen once a year or so back around 1948 are now happening every 9 months. This is particularly true in the northeast, as New England saw an 85 percent increase in heavy precipitation and the Mid-Atlantic saw a 55 percent increase. (The authors defined “extreme storms” as “those expected to occur no more than once per year on average at a particular location based on the historical record,” or the 64 highest precipitation totals for a 24-hour period at each weather station.)
The reason is pretty simple: “Warmer temperatures cause more evaporation, and warmer air holds more water, intensifying the water cycle,” they write.