<a href="http://www.shutterstock.com/cat.mhtml?lang=en&language=en&ref_site=photo&search_source=search_form&version=llv1&anyorall=all&safesearch=1&use_local_boost=1&autocomplete_id=&search_tracking_id=zJCFj1SKQthGXMoZ_yeTPg&searchterm=LGBT&show_color_wheel=1&orient=&commercial_ok=&media_type=images&search_cat=&searchtermx=&photographer_name=&people_gender=&people_age=&people_ethnicity=&people_number=&color=&page=1&inline=337429295">NEGOVURA</a>/Shutterstock
The number of transgender Americans may be twice as big as we thought. According to a new analysis of state and federal data, an estimated 1.4 million adults in the United States, or 0.6 percent of the total population, identify with a gender that does not match their birth sex.
The analysis by the Williams Institute at UCLA comes as policymakers increasingly consider questions of transgender rights in schools, workplaces, and the military.
Previously, the most widely accepted estimate suggested 0.3 percent of American adults were transgender. That figure came from a smaller analysis by the Williams Institute in 2011, based on a health survey in Massachusetts and a survey about tobacco use among LGBT people in California. The new analysis draws on a much bigger set of data from 19 states that have since started asking about gender identity in questionnaires about health risk behaviors run by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The researchers also used Census Bureau data to estimate the transgender populations in the 31 other states.
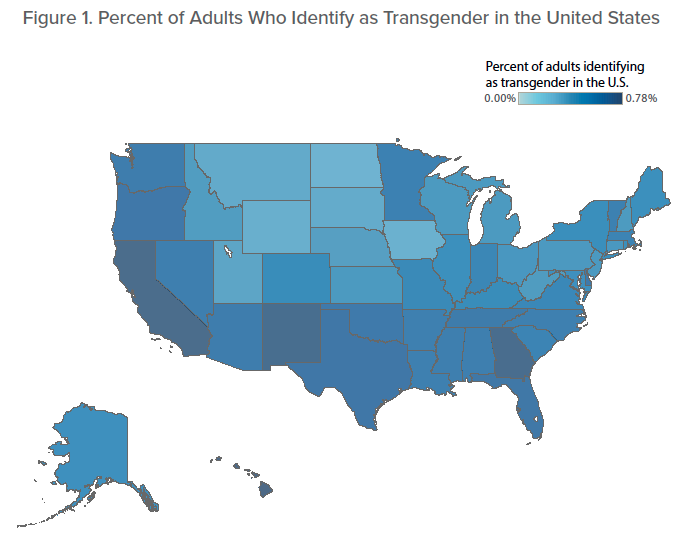
The study’s authors say their analysis is the first in the United States to estimate the transgender population in each state. Hawaii, California, Georgia, and New Mexico had the biggest percentages of adults who identified as transgender, at 0.8 percent each. North Dakota, Iowa, Wyoming, Montana, and South Dakota had the smallest percentages, at about 0.3 percent each. Young adults between the ages of 18 and 24 were most likely to identify as transgender (0.7 percent), compared with 0.6 percent of those between the ages of 25 and 64 and 0.5 percent of adults older than 64.
The District of Columbia had a far higher rate of transgender identity than any state in the study, at an estimated 2.8 percent of adults.
The Census Bureau does not ask about gender identity in its population count, so we still don’t know exactly how many Americans identify as transgender. In May, Rep. Raúl Grijalva of Arizona introduced a bill that would require federal agencies to include questions about gender identity in national demographic surveys.
“The findings from this study are critical to current policy discussions that impact transgender people,” says Jody Herman, one of the study’s authors. “Policy debates on access to bathrooms, discrimination, and a host of other issues should rely on the best data available to assess potential impacts, including how many people may be affected.”

















